Crop coefficient
Models of transpiration, or combined evapotranspiration (ET), from plants often combine an idealized or well calibrated reference crop response model with coefficients that account for differences in response observed for the crop of interest. The most basic crop coefficient, Kc, is simply ratio of ET observed for the crop studied over that observed for the reference crop under the same conditions.
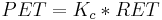
Potential evapotranspiration (PET), is the evaporation and transpiration that potentially could occur if a field of the crop had an ideal unlimited water supply. RET is the reference ET often denoted as ETo.
Even in agricultural crops, where ideal conditions are approximated as much as is practical, plants are not always growing (and therefore transpiring) at their theoretical potential. Plants have growth stages and states of health induced by a variety of environmental conditions.
RET usually represents the PET of the reference crops most active growth. Kc, then becomes a function or series of values, specific to the crop of interest through its growing season. These can be quite elaborate in the case of certain corn varieties, but tend to use a trapezoidal or a leaf area index (LAI) curve for common crop or vegetation canopies.
Stress coefficients, Ks, account for diminished ET due to specific stress factors. These are often assumed to combine by multiplication.
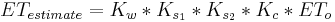
Water stress is the most ubiquitous stress factor, often denoted as Kw. Stress coefficients tend to be functions ranging between 0 and 1. The simplest are linear, but thresholds are appropriate for some toxicity responses. Crop coefficients can exceed 1 when the crop evapotranspiration exceeds that of RET.
References
Allen, R.G.; Pereira, L.S.; Raes, D.; Smith, M. (1998). Crop Evapotranspiration—Guidelines for Computing Crop Water Requirements. FAO Irrigation and drainage paper 56. Rome, Italy: Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. ISBN 92-5-104219-5. http://www.fao.org/docrep/X0490E/x0490e00.HTM. Retrieved 2007-11-24.